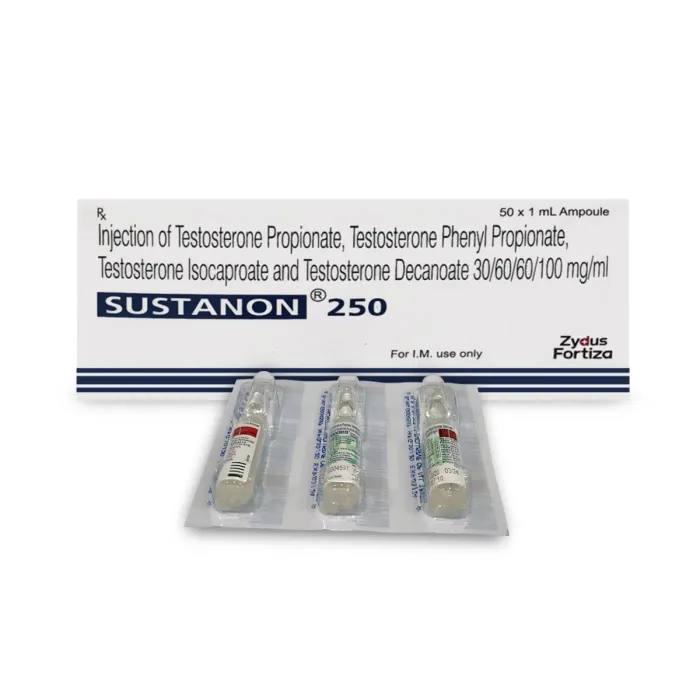
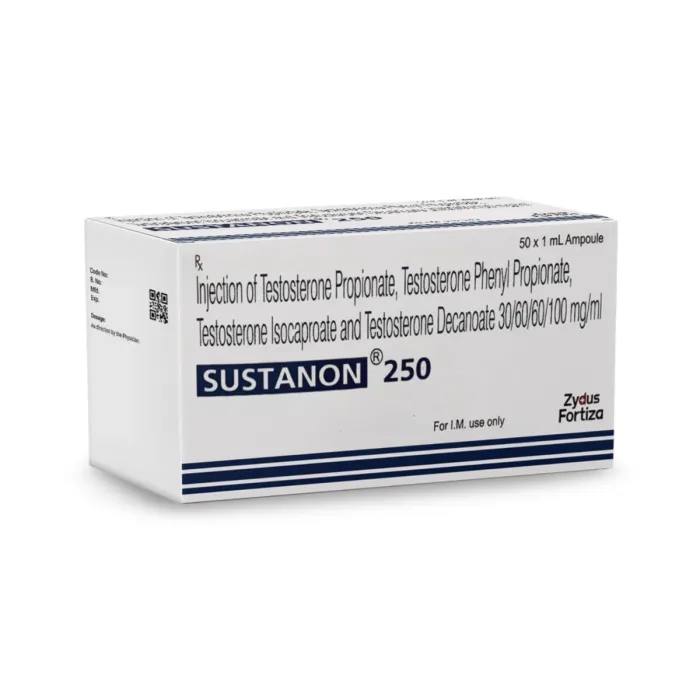
Sustanon 250 is a prescription-only injectable medication containing a blend of four different testosterone esters used primarily for testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) in men with hypogonadism.
What is Sustanon 250?
Sustanon 250 is an androgen, a type of anabolic steroid. Each 1 mL ampoule or vial contains a pale yellow oily solution with 250 mg of total testosterone (176 mg as pure testosterone) derived from a mix of four esters:
Testosterone propionate (30 mg)
Testosterone phenylpropionate (60 mg)
Testosterone isocaproate (60 mg)
Testosterone decanoate (100 mg)
The combination of short-acting (propionate, phenylpropionate) and long-acting (isocaproate, decanoate) esters provides a rapid onset of action and prolonged duration, maintaining testosterone levels for up to three weeks.
Uses
Sustanon 250 is approved for the treatment of male hypogonadism (a condition where the body does not produce enough testosterone), to help alleviate associated symptoms:
Impotence and erectile dysfunction
Decreased libido (sex drive)
Infertility caused by sperm production disorders
Fatigue and depression
Loss of muscle mass and bone mineral density (osteoporosis)
It is also used in female-to-male transgender individuals to develop male sexual characteristics.
Administration and Dosage
Sustanon 250 is administered by deep intramuscular injection, typically into the buttock, upper leg, or upper arm. It should not be self-administered; a doctor or nurse usually performs the injection. The typical dosage for TRT is 1 mL (one injection) every three weeks, but the precise dose and frequency are determined by a doctor based on individual patient response and blood testosterone measurements.
Important Precautions and Side Effects
Contraindications: Sustanon 250 should not be used in men with known or suspected prostate or breast cancer.
Allergies: The injection contains arachis (peanut) oil and benzyl alcohol, so it is contraindicated in individuals with peanut or soy allergies.
Side Effects: Common side effects can include weight gain, increased red blood cell count, increased prostate-specific antigen (PSA) levels, and injection site reactions. Chronic overdose symptoms, such as frequent or persistent erections (priapism), require medical attention and a dosage reduction.
Monitoring: Regular medical monitoring, including blood tests for testosterone levels and screening for prostate issues, is essential during treatment.


Reviews
There are no reviews yet.